Welcome back to another SecuringNinja tutorial. No cyber security researcher should be with out a database to practice their skills on, or just to store tons of relational data. Today we will show you how to install MySQL on a Mac. Having a local database is perfect for running websites locally, or for providing persistent storage for another application.
The MySQL Shell is an interactive Javascript, Python, or SQL interface supporting development and administration for the MySQL Server and is a component of the MySQL Server. You can use the MySQL Shell to perform data queries and updates as well as various administration operations. The MySQL Shell provides: Both Interactive and Batch operations. Download MySQL Community Server 5.5 DMG Archive.; Double-click the DMG Archive, and then double-click the.pkg file that starts with mysql-5.5.Follow the instructions to install the MySQL server.; Double-click the MySQLStartupItem.pkg file, and follow the instructions in the setup wizard. The wizard installs the MySQL server as an auto-startup item.
In this article we cover how to:
MySQL is very straight forward to install on a Mac. If you do not already have the Homebrew package manager for Mac you’ll need to install that first. If you would rather not install Homebrew you can also install MySQL using the DMG file available on the MySQL site.
Installing Homebrew on Mac
Lets start by opening up Terminal and installing Homebrew. Homebrew is a macOS package manager that makes installing packages on macOS a breeze.
To install Homebrew on Mac run the following command:
Once the install is complete go ahead and run an update to test that everything is working correctly.
Start Mysql Mac
With Homebrew installed it is a simple matter to install MySQL.
Installing MySQL on Mac with Brew
Installing MySQL with Brew is a breeze. All it takes is:
This will install the most recent version of the package available on Brew. As of this writing it is MySQL version 8.0. To install a different version simply append the version to the end of the package with an @ symbol. For example, to install MySQL 5.7 use:
If you don’t want to install Homebrew you can also install MySQL with the DMG file available for download as described below.
Installing MySQL with a DMG file
You can also install MySQL via the DMG file on the MySQL downloads page. This will add a MySQL preference pane in System Preferences as well. You can start and stop your server from here too.
First begin by downloading and mounting the DMG file available from the MySQL Community downloads page. Make sure you grab the appropriate DMG for your OS version.
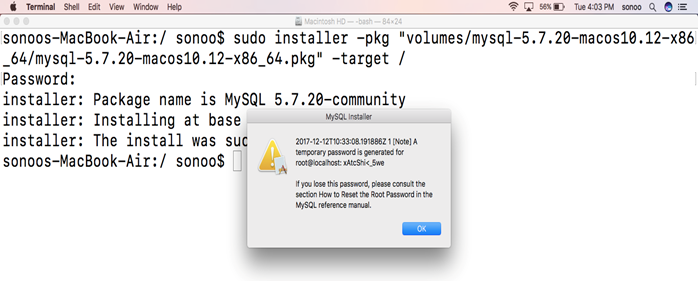
Mount the DMG and double click the .pkg file to begin the installation.
Step through the installer installer and make a note of your temporary root password. You will need this for the initial connection to the server. DO NOT LOSE IT!
The server will require that you update your password on the first login. MySQL server is now installed. To start the server use launchctl or the MySQL preference pane in System Preferences. The server uses very few resources while running in the background so there really is no need to start and stop the server each time.
To start the server via launchctl:
This instructs MySQL to start when the system boots up.
You can also start and stop MySQL through the System Preferences pane. Open System Preferences and select MySQL:
And finally, start or stop the server as needed.
From this preference pane you can also edit the MySQL server configuration, re-initialize the database, and uninstall MySQL server entirely. We cover how to uninstall MySQL on Mac in the next section.
Uninstalling MySQL on Mac
If you installed MySQL via the DMG file method then uninstalling is extremely straight forward. Navigate to the MySQL preference pane in System Preferences, and click Uninstall. Thats it! MySQL has been uninstalled.
If you however installed MySQL using the Brew method described above, then there are a couple of extra steps.
Uninstalling MySQL on Mac with Brew
The steps below show how to uninstall MySQL installed with Brew. Begin by finding any running MySQL processes and stopping them. Then uninstall MySQL and remove all files.

Download Mysql For Mac Using Terminal Download
What to do with your new database
Now that you’ve got a local database up and running you may want to take a look at how a SQL injection attack works. Your new database will be great for practice! If you have any issues getting your database up and running, please reach out in the comments below. We would love to assist you!
In this tutorial, we are going to learn how to install MySQL community server on Mac and setting up the MySQL in Terminal app.Mac OS doesn’t come along with the pre-configured version of MySQL, but this step by step guide will make the task easy for you. By the end of this tutorial, you will be able to set up the MySQL server on your Mac system for local development purposes.
Download MySQL Server
Before we start installing MySQL server on mac, we first download the latest version of MySQL from its official site.
Visit https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/mysql and choose the MySQL version that you want to download.
On this page, you will see list of operating systems under the “Select Operating System” dropdown choose the macOS from the list. Then, click on the download button for the MySQL .dmg file. You can download the other MySQL instances as per your operating system requirement.
Install MySQL on Mac
You have to click on the MySQL file to install the MySQL on Mac system. You might get the warning “macOS cannot verify that this app is free from malware”.
To get rid from this issue got to System Preferences > Security & Privacy and click on the “Open Anyway” button. This will allow you to install the MySQL version in your system.
Once the MySQL installation is completed, go to System Preferences and click on the MySQL icon that you can see on the bottom left position.
Here you can see the MySQL is already running and other configurations of MySQL. You can even stop the server by clicking on “stop MySQL server”. Well this is not the only way to start the server, we can even manually start the MySQL server via command line.
Configure MySQL in Mac for Terminal App
To start the MySQL via terminal app, you need to use the following command.
But this command will display the following error on your terminal screen.
“command not found: mysql.server”
To fix this issue, we have to define the MySQL path in the paths file. The easiest way to open the file is to type the following command in the terminal and provide the password.
Include one per line given below paths in the /etc/paths file.
Next, type the command to start the MySQL server.
Here is the output we get when MySQL is started correctly.
We used `sudo` with mysql.server start otherwise it will throw permission errors.
Important MySQL Commands
Here are the important commands that are often used while working with MySQL.
Run the following command to stop mysql server:
Type the below command to restart the MySQL server that is already running:
To verify the current status of MySQL server:
Access Root via Mac Terminal & Create Database
Now, we have reached to essential step of our tutorial. We are all set with the server configurations, now we have to access the MySQL root. When you run the following command it will ask for the password. So you have to type the password that you defined when installing the MySQL initially.
Mysql Server For Mac
Now we will use the mysql query to create a new database.
You can verify the newly created MySQL database.
Use the newly created “positrondb” db by using the below command.
Create a table in the MySQL database =>‘positrondb’.
Verify the table in the database.
Summary
We have completed the MySQL tutorial, and In this tutorial, we learned how to install MySQL community server on Mac OS, How to access root user in the MySQL server, Create Database and Table.
I hope you liked this tutorial, dont forget to share it with others.